Photoplethysmography - How the Apple Watch measures your heart rate for the Non-Technical
By shooting a blinking green light (hundreds of times per second) into your wrist a powerful SIP in the Apple Watch processes the data that measures your heart rate
The heart rate sensor in the Apple Watch uses what is known as photoplethysmography.
Terms for the Non-technical
:)🙋your welcome:)
The change in volume [of blood in your wrist] caused by the pressure pulse is detected by illuminating the skin with the GREEN light from a light-emitting diode (LED) and then measuring the amount of light either transmitted or reflected to a photodiode. Each cardiac cycle appears as a peak, as seen in the figure. Because blood flow to the skin can be modulated by multiple other physiological systems, the PPG can also be used to monitor breathing, hypovolemia, and other circulatory conditions.[2] Additionally, the shape of the PPG waveform differs from subject to subject, and varies with the location and manner in which the pulse oximeter is attached.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cZPwTdC3ShU)
Terms for the Non-technical
:)🙋your welcome:)SIP (WHAT IS SIP) - System in Package
The SiP in Apple Watch Series 1 contains a dual-core CPU with the graphics processor (GPU)
its processes all the data and samples rates coming from your apple watch sensors)
Terms for the Non-technical
:)🙋your welcome:)
The Apple Watch Infra LED (red light)
the purpose of the IR LED is to basically detects blood through your the thickness of your skin
ALSO DID YOU KNOW - IR can also detect through paint
How the Apple Watch measures your heart rate for the Non-Technical
(The quick one sentence answer:
Blood is red because it reflects red light
and absorbs green light.
- a blinking GREEN Light shoots into your wrist and a sensor measures the light coming back!
Fig. 1.1 Green LED light reflection (~510nm)
The green light absorption (~510 nm) is greater when your heart beats during blood flow throughout your your wrist andHOWEVER
Between beats the green light absorption is alot less - (there is less green light being absorbed by the body)do not confuse "the ABSORPTION of green light" with the wavelength of green light (~510nm) and also don't forget your trig equations (the location of green light bulb click here)
So by shooting a blinking green light (hundreds of times per second) into your wrist a powerful SIP in the Apple Watch processes the data that measures your heart rate
👰Whoa - way too technical to for the non-techs
SIP (WHAT?) WHAT IS SIP -
System in Package
The SiP in Apple Watch Series 1 contains a dual-core CPU with the graphics processor (GPU) It processes all the data and samples rates coming from your apple watch sensors)
Why Green? Why not Purple (I like purple light)
Who doesn't like purple light or what is also known as "indigo" or a "black light".
source NASA.GOV
Indigo appears between blue and violet in a rainbow. Purple grapes and blueberries are indigo
source NASA.GOV
Indigo appears between blue and violet in a rainbow. Purple grapes and blueberries are indigo
😎Purple Lights - "They are great at parties"
However a green light shooting out an LED is more useful.
Fig 1.2 Sensor Example and Datasheet Source:
http://www.mouser.com/ds/2/321/28380-ColorPAL-Documentation-370265.pdf
Fig 1.2 Sensor Example and Datasheet Source:
http://www.mouser.com/ds/2/321/28380-ColorPAL-Documentation-370265.pdf
Here is why... Tell me more...
The Apple Watch uses green LED lights paired with
light‑sensitive photodiodes to detect the amount of blood flowing
through your wrist at any given moment. When your heart beats, the blood
flow in your wrist — and the green light absorption — is greater.
Between beats, it’s less. By flashing its LED lights hundreds of times
per second, Apple Watch can calculate the number of times the heart
beats each minute — your heart rate. In addition, the heart rate sensor
is designed to compensate for low signal levels by increasing both LED
brightness and sampling rateThe heart rate sensor in Apple Watch uses what is known as photoplethysmography.
Blood is red because it reflects red light and absorbs green light.
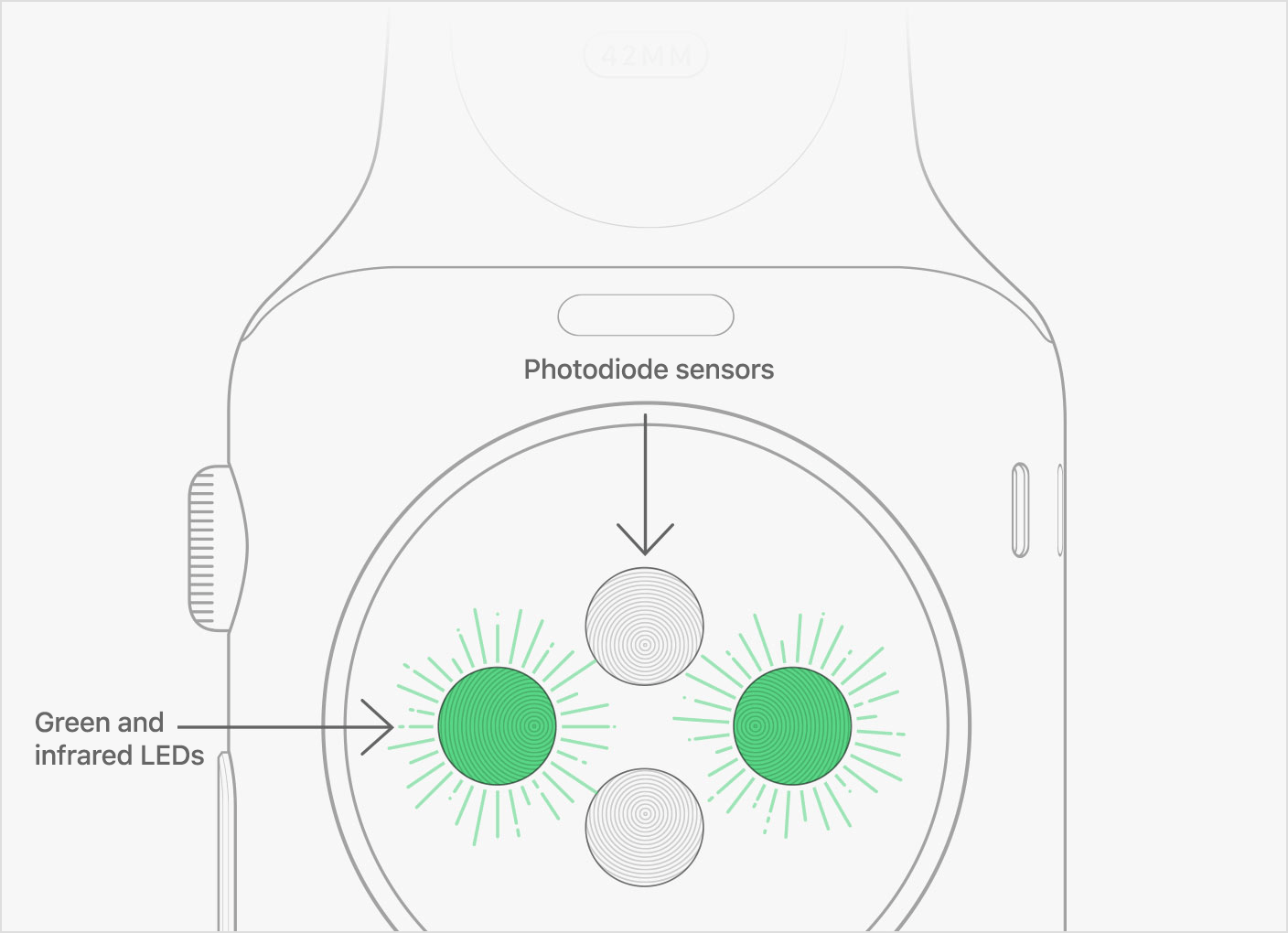
The heart rate sensor can also use infrared light. This
mode is what Apple Watch uses when it measures your heart rate in the
background.
For best results, start with a good fit
Even under ideal conditions, Apple Watch may not be able to get a reliable heart rate reading every time for everybody. And for a small percentage of users, various factors may make it impossible to get any heart rate reading at all. But there are things you can do to help Apple Watch get the most consistent and best heart rate readings possible.Too loose
If your Apple Watch doesn’t stay in place, or the sensors aren’t reading your heart rate, tighten the band a bit.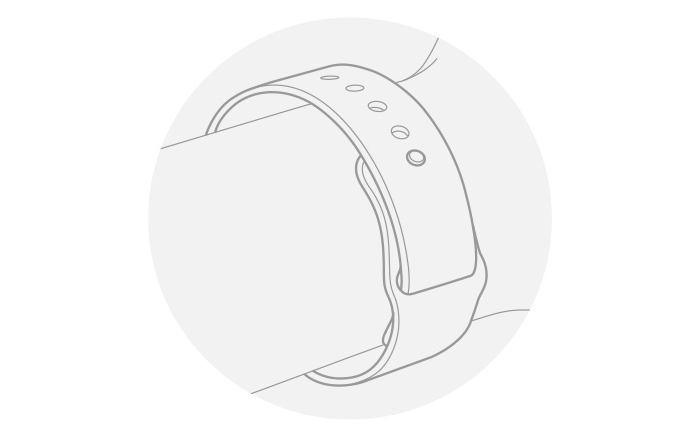
Just right
Your Apple Watch should be snug but comfortable.
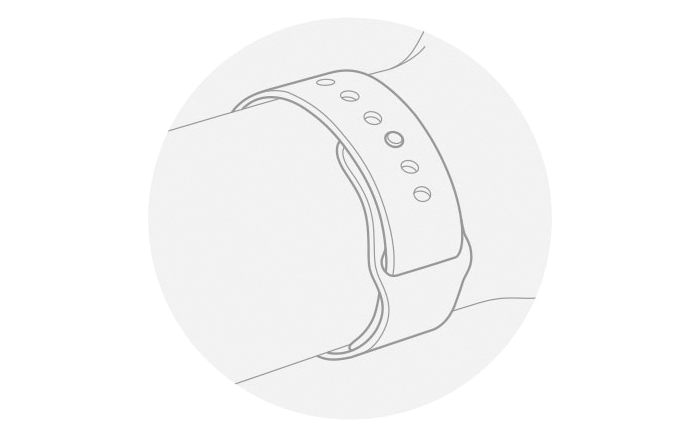
What else affects your reading
Many factors can affect the performance of the Apple Watch heart rate sensor. Skin perfusion is one. A fancy way of describing how much blood flows through your skin, skin perfusion varies significantly from person to person and can also be impacted by the environment. If you’re exercising in the cold, for example, the skin perfusion in your wrist may be too low for the heart rate sensor to get a reading.Motion is another factor that can affect the heart rate sensor. Rhythmic movements, such as running or cycling, give better results compared to irregular movements, like tennis or boxing.
Permanent or temporary changes to your skin, such as some tattoos, can also impact heart rate sensor performance. The ink, pattern, and saturation of some tattoos can block light from the sensor, making it difficult to get reliable readings.
If you’re not able to get a consistent reading because of any of these factors, you can connect your Apple Watch wirelessly to external heart rate monitors such as Bluetooth chest straps.
When doing an Open Water Swim* in the Workout app, water may prevent a heart rate measurement, but Apple Watch will still track your calories using the built-in accelerometer. When doing a Pool Swim* in the Workout app, water may prevent a heart rate measurement, but Apple Watch will still track your calories, laps, and distance using the built-in accelerometer.
Heart rate is just one of many factors that Apple Watch
uses to measure your activity and exercise. Depending on your workout,
it selects the most appropriate inputs for that activity. For example,
when you’re running indoors, it also uses the accelerometer. When you’re
cycling outdoors, it uses the GPS in your Apple Watch Series 2 or in
your iPhone for your Apple Watch (1st generation). And even when you’re
not in a dedicated workout, it tracks how much you move each day. So
Apple Watch can give you the information — and the motivation — to
improve your fitness and your health.
* Available on Apple Watch Series 2 only. Apple Watch Series 1 and Apple Watch (1st generation) aren't suitable for swimming.
* Available on Apple Watch Series 2 only. Apple Watch Series 1 and Apple Watch (1st generation) aren't suitable for swimming.




No comments:
Post a Comment